News & Blogs
In this blog, we touch on diverse topics about Japanese food cultures, practices together with the culinary secret, TREHA®, and its important role in the Japanese food industry. We hope our blog helps you obtain in-depth knowledge of the secrets and science behind Japanese cuisine, shared from our kitchen, to yours.
What do you imagine when you hear the word ‘sugar’? “It’s sweet.” Or “it has calories”, - but what else? Beyond its sweetness, sugar is also responsible for creating many important physical properties in the foods we love, including creating the perfect texture and extending shelf life.
The role of sugar
Sweet taste: Sugar sweetens food products.
Developing physical structure: Food yield is decreased when sugar is reduced.
Adjusting texture: When dissolved in food, sugar enhances a soft, smooth texture. When crystalized in food, it creates a crispy or granular texture.
Creating color and aroma: Sugar reacts with other food ingredients to deliver aroma and enhances browning.
Retaining moisture: Sugar helps to maintain the quality of food. It inhibits syneresis and drying of food by stabilizing water molecules.
Inhibiting fatty acid oxidation: Sugar inhibits discoloration and unpleasant odor from fatty acid oxidation.
Inhibiting starch retrogradation: Sugar maintains softness and moisture in foods.
Inhibiting protein denaturation: Proteins like meat and egg coagulate more slowly when heated with sugar.
Preservation: Sugar slows down food deterioration when it is incorporated into the structure of food.
Providing energy: Sugar is one of major source of calories.
Physiological functions: Some sugars have the unique ability to pass through the gut undigested to provide intestinal benefits, assist in controlling blood sugar after a meal, and are lower in calories than table sugar.

Function of sugar showcased in strawberry jam.
Comparison of strawberry jam
Three types of strawberry jam are compared.
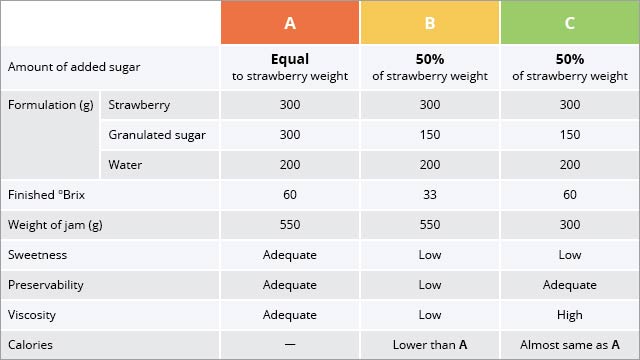

A is classic strawberry jam – using the same amount of sugar as strawberries. It has adequate sweetness, viscosity, and preservability.
B has lower viscosity and preservability, because amount of sugar is half of A. Sugar plays an important role in improving preservability. It reduces the availability of free water available for microorganisms to grow.
C is made by reducing B to the same °Brix as A. Although preservability becomes almost the same as A, C has high viscosity derived from the larger proportion of strawberries.
Not only taste, but physiological properties and preservability are controlled by sugar content.
The type of sugar will affect the color of the pineapple syrup.
Color comparison of pineapple syrups
Pineapple syrup samples were heated to 85℃/185ºF for 20 minutes. When compared to sucrose, TREHA® is more stable in acid and heat, and is unlikely to discolor, making it ideal for many different applications, including preserves.

Starch syrup can also be a suitable ingredient for maintaining sugar content without adding too much sweetness. However, starch syrup has a variety of sweetness, viscosity and moisture content to be considered.
Thank you very much for reading our blog. We, Nagase Food Ingredients, have the practical know-how for using sugar. Our experienced staff can help you to create and review your menus. Feel free to contact us.
Did you find this blog interesting?
Please share it with your friends in the food service industry.
We regularly update the blog about the food culture of Japan, where TREHA® was discovered for culinary applications.
Click here and send us a message to subscribe.
Or hit us up on Instagram @trehalose_sensei!

